Developed and written by Maximiliano Pizarro - Specialist Solution Architect at Red Hat LATAM
🚀 Quick Start Recommendation
For the best experience, we recommend forking this repository to your own GitHub organization or user account. This allows you to:
- Customize configurations without affecting the original repository
- Set up your own GitOps workflows with ArgoCD pointing to your fork
- Modify cluster-specific settings (like domain names) in your own repository
- Maintain your own version control and deployment pipeline
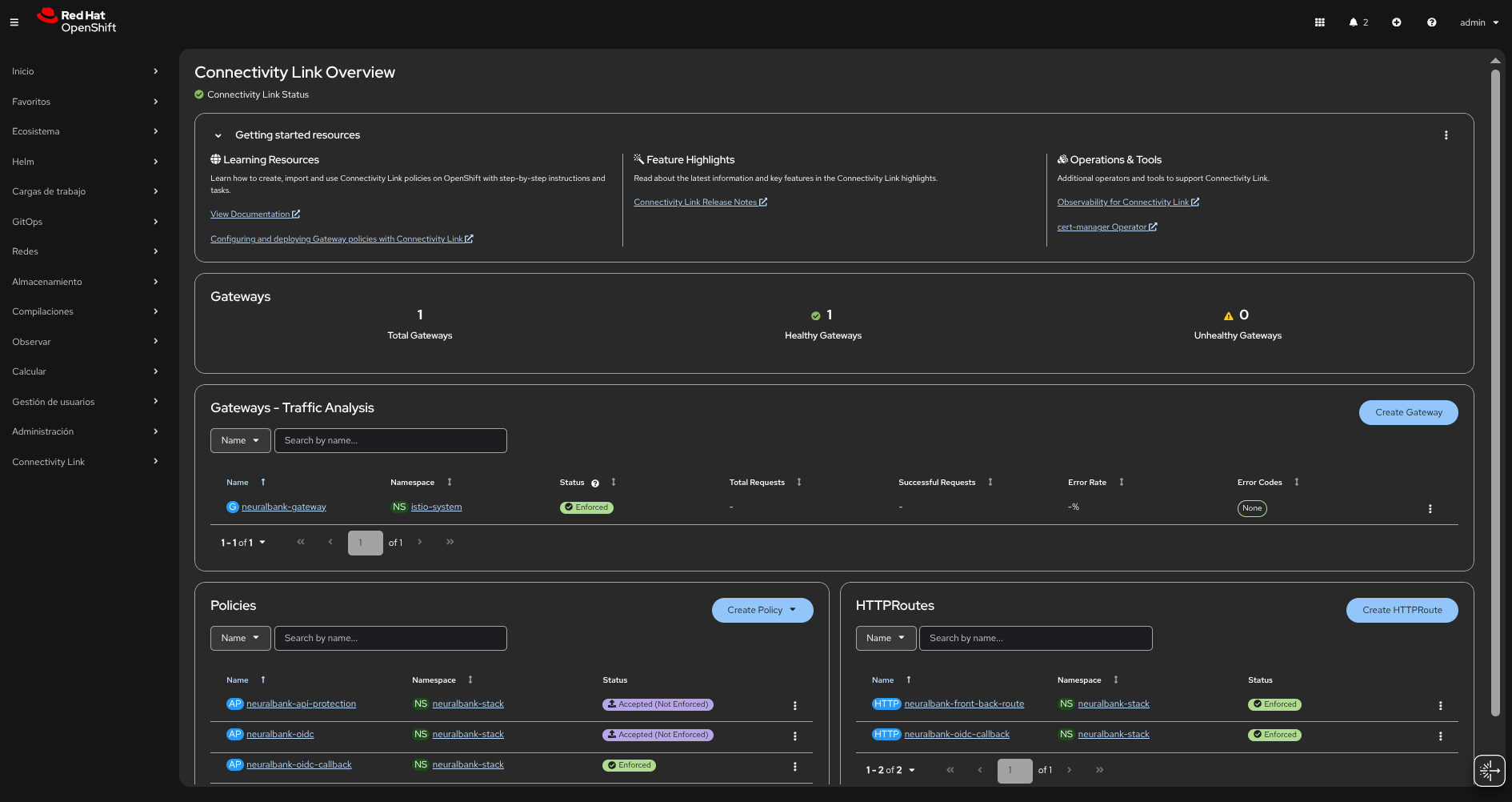
After forking, update the repository references in applicationset-instance.yaml to point to your fork.
📋 TL;DR
- Requirements: OpenShift 4.20+, Python 3.11+, OpenShift CLI (
oc), Ansible Core, cluster-admin privileges - Installation Method: Automated via
install.sh(updates cluster domain in all manifests, then runs Ansible playbook) - Quick Start: Run
./install.shto install GitOps operator and deploy all applications (or runansible-playbook install-gitops.yamlafter updating domain references) - Manual Alternative: Install OpenShift GitOps operator, update cluster domain in manifests, then
oc apply -f applicationset-instance.yaml - Outcome: ArgoCD manages all components; Connectivity Link via dynamic console plugin (Administration → spec.plugins); OIDC client secret obtained from Keycloak by the playbook
📖 Overview
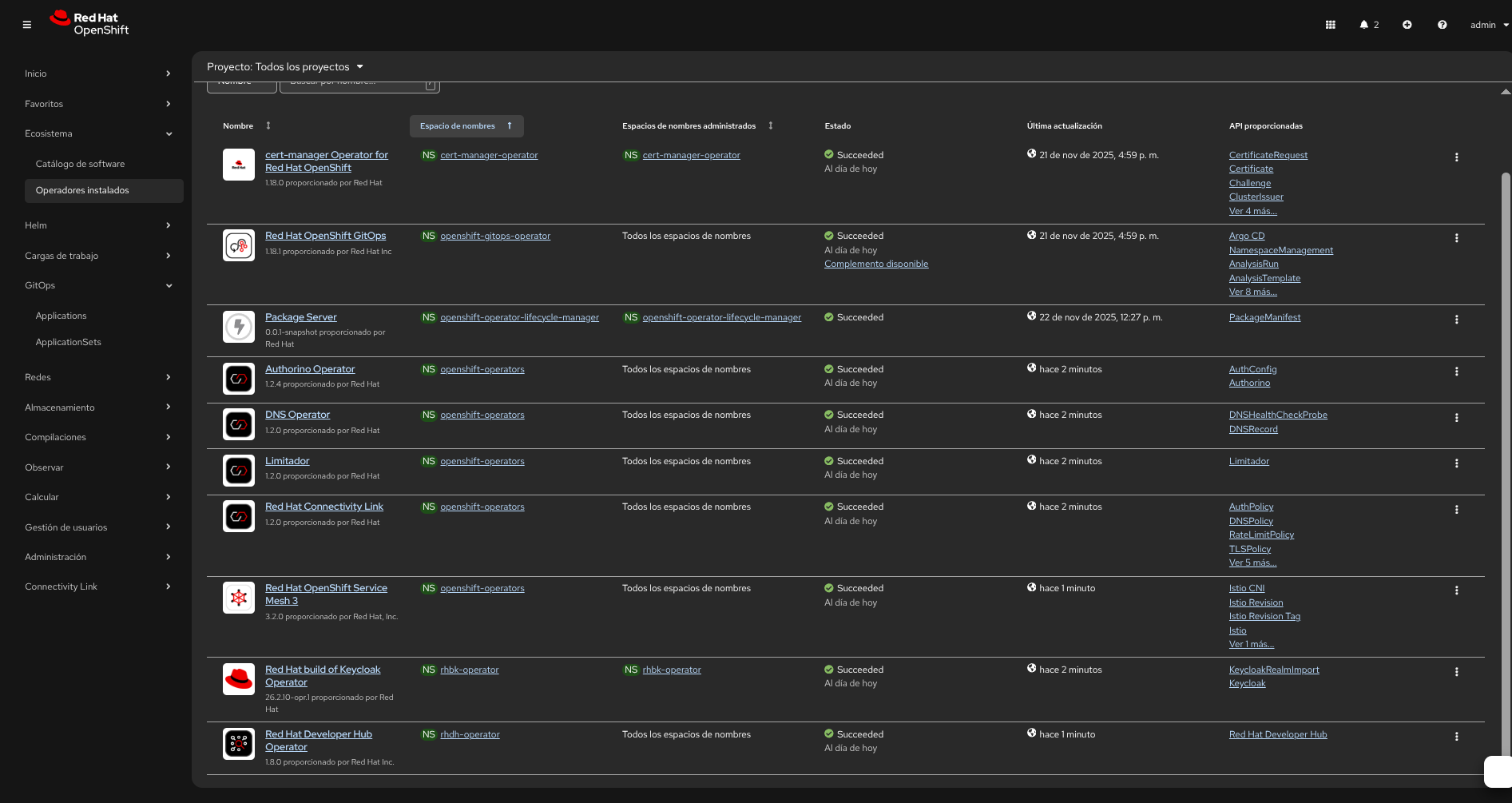
This repository contains a comprehensive demo of Connectivity Link using a GitOps workflow. It demonstrates how applications and infrastructure are declared as Kubernetes/Helm manifests and managed with ArgoCD (OpenShift GitOps). The demo includes:
- Service Mesh: Istio-based service mesh for traffic management and security
- API Gateway: Kubernetes Gateway API implementation with Istio
- Authentication: Keycloak for identity and access management
- Authorization: Kuadrant/Authorino for OIDC-based API protection via OIDCPolicy
- Application Stack: NeuralBank demo application (frontend, backend, database)
- Developer Hub: Red Hat Developer Hub (Backstage) integration
- Automated Installation: Ansible playbook for complete infrastructure provisioning
Key Components
- Connectivity Link: A set of configurations and examples demonstrating connectivity between components (services, gateways, and authentication) within an OpenShift cluster in a GitOps context
- OpenShift GitOps (ArgoCD): Used as the GitOps controller to reconcile the declared state in this repository with the cluster
- Service Mesh Operator: Manages the Istio service mesh control plane and data plane
- RHCL Operator: Red Hat Connectivity Link operator for managing connectivity policies and OIDC authentication
- Ansible Automation: Automated installation playbook that ensures proper operator installation order and verification
Architecture Overview
The architecture follows a consolidated ApplicationSet approach where all infrastructure components, operators, and applications are managed through a single applicationset-instance.yaml file. This simplifies deployment and ensures proper installation order through sync_wave annotations.
Installation Order (by sync_wave):
- Wave 0: OpenShift GitOps operator installation
- Wave 1: Namespaces creation
- Wave 2: Operators (rhbk-operator, RBAC configurations)
- Wave 3: Infrastructure components (Service Mesh, RHCL Operator, Developer Hub)
- Wave 4-7: Applications (NeuralBank Stack, LiteMaaS, etc.)
⚙️ Important Requirements
- OpenShift version: 4.20+ (this demo and manifests are validated against this version)
- Python: 3.11+ (required for Ansible Core and collection dependencies)
- OpenShift CLI (
oc): Installed and logged in to the target cluster (oc version,oc whoami) - Ansible: Ansible Core plus collections
kubernetes.coreandcommunity.kubernetes(see README-INSTALL.md) - Permissions: cluster-admin privileges are required to install the GitOps operator, create namespaces, and let ArgoCD manage cluster resources
🔧 Configuration: Pre-configure DNS with ApplicationSets
⚠️ Important: This repository contains demo cluster domain references (apps.cluster-wjvhz.dynamic.redhatworkshops.io) that must be updated to match your OpenShift cluster’s base domain before deployment.
Instead of manually updating cluster domain references, you can pre-configure the DNS hostnames directly in the ApplicationSet definitions. This approach uses Kustomize patches and Helm parameters to dynamically inject your cluster domain values at deployment time.
Automatic Domain Update
We provide a bash script to automatically replace all cluster domain references:
chmod +x update-cluster-domain.sh
./update-cluster-domain.sh <your-cluster-base-domain>
Example:
./update-cluster-domain.sh apps.your-cluster.example.com
The script will:
- Find all YAML files containing the demo cluster domain
- Replace them with your cluster’s base domain
- Show a summary of updated files
Manual Domain Update
If you prefer to update manually, search and replace apps.cluster-wjvhz.dynamic.redhatworkshops.io with your cluster’s base domain in the following locations:
neuralbank-stack/values.yaml- Keycloak and application URLsrhcl-operator/- OIDC policies and route configurationsservicemeshoperator3/- Gateway route hostnamesrhbk/- Keycloak hostname and redirect URIs
Finding Your Cluster Domain
First, find your OpenShift cluster’s base domain:
oc get ingress.config/cluster -o jsonpath='{.spec.domain}'
Or check your cluster’s console URL - it typically follows the pattern: console-openshift-console.apps.<your-cluster-domain>
Option 1: ApplicationSet with Kustomize Patches (Recommended)
This approach uses Kustomize patches to update DNS hostnames in Keycloak, Routes, and OIDC policies. Update the keycloak_host and app_host values in the generator elements:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ApplicationSet
metadata:
name: connectivity-infra-plain
namespace: openshift-gitops
spec:
goTemplate: true
generators:
- list:
elements:
- name: namespaces
namespace: openshift-gitops
path: namespaces
sync_wave: "1"
- name: operators
namespace: openshift-gitops
path: operators
sync_wave: "2"
- name: developer-hub
namespace: developer-hub
path: developer-hub
sync_wave: "2"
- name: servicemeshoperator3
namespace: openshift-operators
path: servicemeshoperator3
sync_wave: "3"
- name: rhcl-operator
namespace: openshift-operators
path: rhcl-operator
sync_wave: "3"
template:
metadata:
name: ''
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: 'https://github.com/maximilianoPizarro/connectivity-link.git'
targetRevision: main
path: ''
destination:
server: 'https://kubernetes.default.svc'
namespace: ''
syncPolicy:
automated:
selfHeal: true
prune: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
---
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ApplicationSet
metadata:
name: connectivity-infra-rhbk
namespace: openshift-gitops
spec:
goTemplate: true
generators:
- list:
elements:
- name: rhbk
namespace: rhbk-operator
path: rhbk
sync_wave: "2"
keycloak_host: rhbk.apps.cluster-24p6f.24p6f.sandbox2386.opentlc.com
app_host: neuralbank.apps.cluster-24p6f.24p6f.sandbox2386.opentlc.com
template:
metadata:
name: ''
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: 'https://github.com/maximilianoPizarro/connectivity-link.git'
targetRevision: main
path: ''
kustomize:
patches:
- target:
group: k8s.keycloak.org
kind: Keycloak
name: rhbk
patch: |-
- op: replace
path: /spec/hostname/hostname
value: ""
- target:
group: k8s.keycloak.org
kind: KeycloakRealmImport
name: neuralbank-full-import
patch: |-
- op: replace
path: /spec/realm/clients/0/redirectUris/0
value: "https:///*"
- target:
group: route.openshift.io
kind: Route
name: neuralbank-external-route
patch: |-
- op: replace
path: /spec/host
value: ""
- target:
group: extensions.kuadrant.io
kind: OIDCPolicy
name: neuralbank-oidc
patch: |-
- op: replace
path: /spec/provider/issuerURL
value: "https:///realms/neuralbank"
- op: replace
path: /spec/provider/authorizationEndpoint
value: "https:///realms/neuralbank/protocol/openid-connect/auth"
- op: replace
path: /spec/provider/tokenEndpoint
value: "https:///realms/neuralbank/protocol/openid-connect/token"
- op: replace
path: /spec/provider/redirectURI
value: "https:///auth/callback"
destination:
server: 'https://kubernetes.default.svc'
namespace: ''
syncPolicy:
automated:
selfHeal: true
prune: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
Key Configuration Points:
keycloak_host: Update this value with your Keycloak hostname (e.g.,rhbk.apps.<your-cluster-domain>)app_host: Update this value with your application hostname (e.g.,neuralbank.apps.<your-cluster-domain>)- The Kustomize patches automatically update all DNS references in Keycloak, Routes, and OIDC policies
Option 2: ApplicationSet with Helm Parameters
For Helm-based deployments, use Helm parameters to inject DNS values. Update the keycloak_host and app_host values in the generator:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ApplicationSet
metadata:
name: connectivity-apps-helm-internal
namespace: openshift-gitops
spec:
goTemplate: true
generators:
- list:
elements:
- name: neuralbank-stack
namespace: neuralbank-stack
path: neuralbank-stack
sync_wave: "5"
keycloak_host: rhbk.apps.cluster-24p6f.24p6f.sandbox2386.opentlc.com
app_host: neuralbank.apps.cluster-24p6f.24p6f.sandbox2386.opentlc.com
template:
metadata:
name: ''
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: 'https://github.com/maximilianoPizarro/connectivity-link.git'
targetRevision: main
path: ''
helm:
parameters:
- name: "keycloak.issuerUrl"
value: "https:///realms/neuralbank"
- name: "keycloak.redirectUri"
value: "https:///auth/callback"
- name: "keycloak.authorizationEndpoint"
value: "https:///realms/neuralbank/protocol/openid-connect/auth"
- name: "keycloak.tokenEndpoint"
value: "https:///realms/neuralbank/protocol/openid-connect/token"
- name: "keycloak.postLogoutRedirectUri"
value: "https://"
destination:
server: 'https://kubernetes.default.svc'
namespace: ''
syncPolicy:
automated:
selfHeal: true
prune: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
Key Configuration Points:
keycloak_host: Update this value with your Keycloak hostnameapp_host: Update this value with your application hostname- Helm parameters automatically inject DNS values into the Helm chart values
Option 3: External Helm Chart ApplicationSet
For external Helm charts, configure the chart repository and version:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ApplicationSet
metadata:
name: connectivity-apps-helm-external
namespace: openshift-gitops
spec:
goTemplate: true
generators:
- list:
elements:
- name: my-app
namespace: my-namespace
helmRepoURL: 'https://example.com/helm'
chart: my-chart
chartVersion: "1.0.0"
sync_wave: "5"
template:
metadata:
name: ''
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: ''
targetRevision: ''
chart: ''
destination:
server: 'https://kubernetes.default.svc'
namespace: ''
syncPolicy:
automated:
selfHeal: true
prune: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
Benefits of Pre-configuring DNS
- No manual file editing: DNS values are configured once in the ApplicationSet
- GitOps-friendly: All configuration is version-controlled in the ApplicationSet manifests
- Dynamic updates: Change DNS values by updating the ApplicationSet and ArgoCD will sync automatically
- Environment-specific: Use different ApplicationSets for different environments (dev, staging, prod)
🚀 Getting Started
Automated Installation (Recommended)
Use the install.sh script: it updates all cluster domain references and then runs the Ansible playbook.
Prerequisites: Python 3.11+, OpenShift CLI (oc), Ansible Core and collections (see README-INSTALL.md).
Run the installation:
chmod +x install.sh
./install.sh
What install.sh does: Pre-flight checks → detects cluster domain → updates domain in applicationset-instance.yaml, rhbk/keycloak.yaml, rhbk/keycloak-neuralbank-realm.yaml, neuralbank-stack/values.yaml, rhcl-operator/oidc-policy.yaml, servicemeshoperator3/gateway-route.yaml → runs install-gitops.yaml.
What the playbook does: Skips GitOps install if already available → Installs OpenShift GitOps (channel only, no version pin; Automatic) → Applies ApplicationSet → Enables dynamic console plugins via spec.plugins → Obtains OIDC client secret from Keycloak (realm neuralbank, client neuralbank) and updates values/oidc-policy and patches OIDCPolicy → Fixes operator configs (rhbk-operator, devspaces).
Manual Installation (Alternative)
If you prefer to install manually:
Step 1: Install OpenShift GitOps Operator
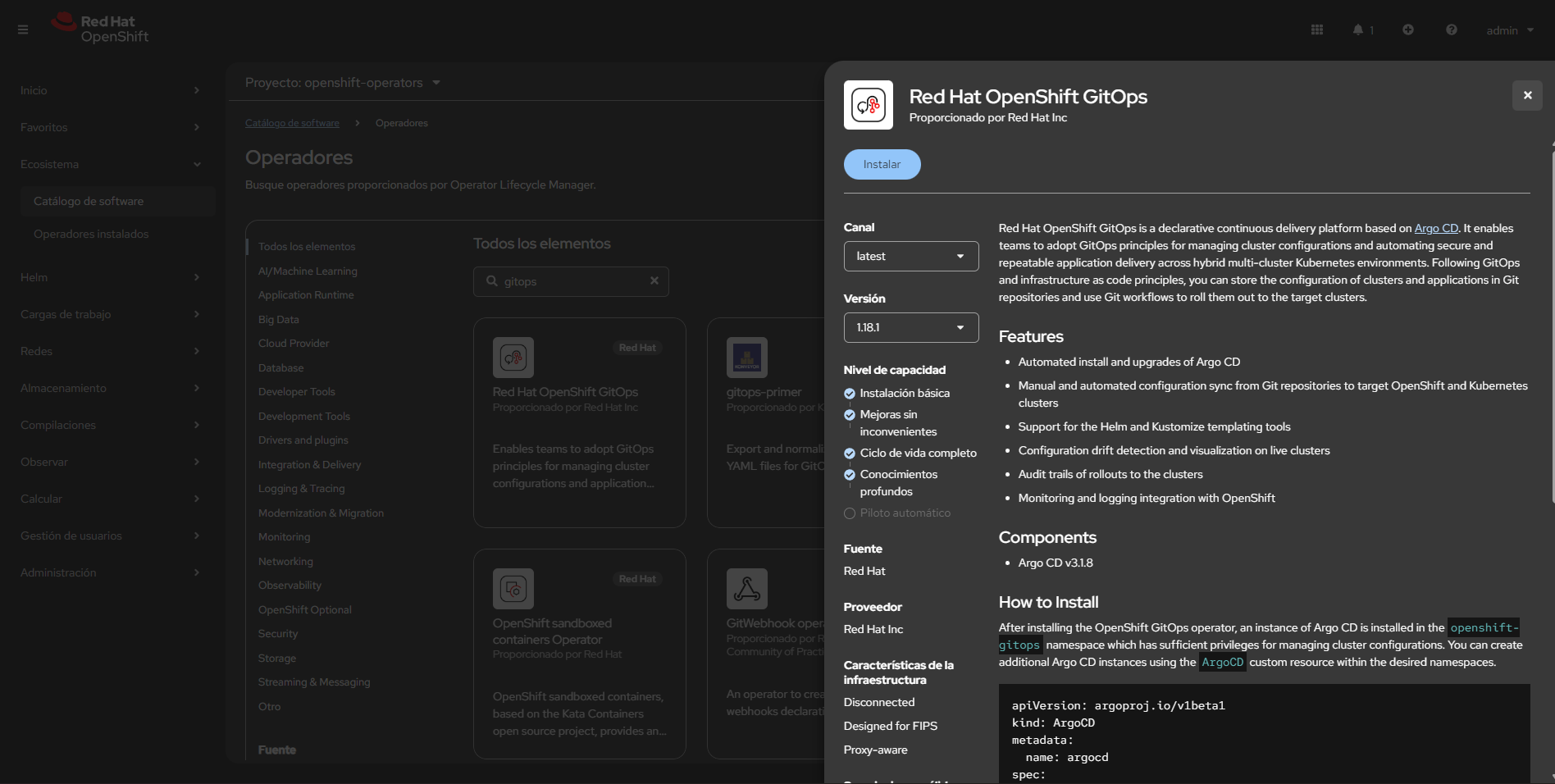
Install the OpenShift GitOps Operator (via OperatorHub in the OpenShift console or via OLM). This is the only manual step required before applying the manifests in this demo.
- Console method: Operators → OperatorHub → search for “OpenShift GitOps” → Install
- CLI alternative: Use
octo install the operator with OLM if you have an appropriate catalog/package available
Step 2: Configure DNS in ApplicationSets (Required)
Before proceeding, pre-configure your cluster domain in the ApplicationSet definitions as described in the Configuration section above. Update the keycloak_host and app_host values in the ApplicationSet generators to match your OpenShift cluster domain.
Step 3: Create ApplicationSet Instance
Create the ApplicationSet / ArgoCD instance using the top-level manifest:
oc apply -f applicationset-instance.yaml
applicationset-instance.yamlcreates/instantiates the applications defined in this repo and points them to this repository for ArgoCD to reconcile- After applying, open the OpenShift GitOps (ArgoCD) console to view status and sync applications if needed
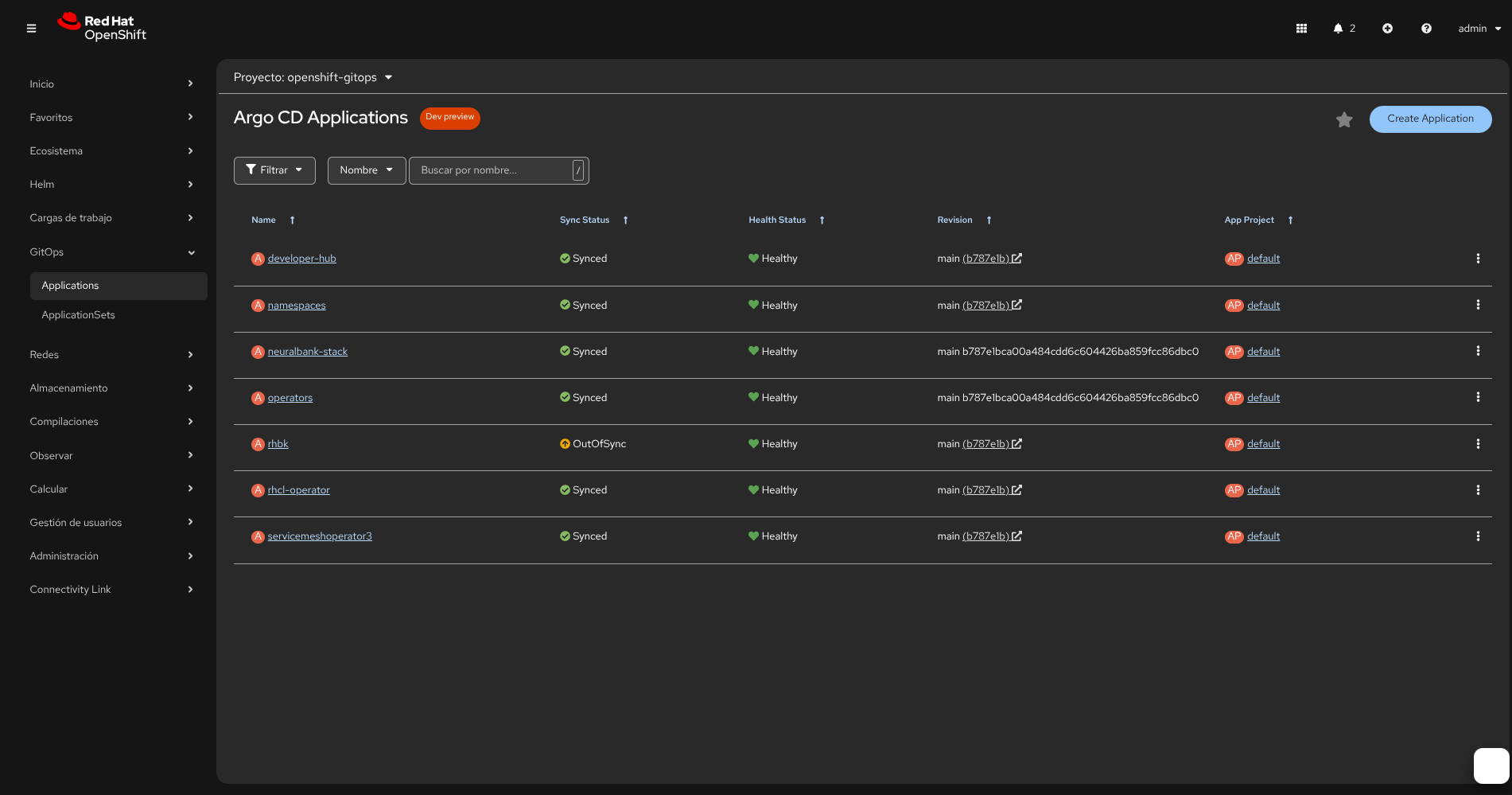
Step 4: Keycloak and OIDC (Automated or Manual)
If you use install.sh and the playbook, the realm neuralbank includes the client neuralbank (confidential). The playbook obtains the client secret from Keycloak and updates values.yaml, oidc-policy.yaml, and patches the OIDCPolicy. Commit and push the updated files so ArgoCD syncs.
If installing manually, configure the client in the Keycloak console after the realm is imported:
Access Keycloak Console:
- Navigate to the Keycloak route (e.g.
rhbk.apps.<your-cluster-domain>) - Log in with admin credentials (
rhbk/keycloak-initial-admin.yaml) - Select the
neuralbankrealm
Configure Client Settings:
For the neuralbank client (or neuralbank-frontend if using that client):
- Navigate to Clients → Select your client (e.g.,
neuralbank) - Enable Client Authentication:
- Set Client authentication to ON (this makes it a confidential client)
- Ensure
publicClientis set tofalsein the configuration
- Enable Direct Access Grants:
- Enable Direct access grants (allows Resource Owner Password Credentials grant type)
- Configure PKCE:
- Set Proof Key for Code Exchange Code Challenge Method to S256
- This enables PKCE (RFC 7636) for enhanced security in authorization code flows
Generate Client Secret:
After enabling client authentication, you need to generate and retrieve the client secret:
- Go to the Credentials tab of your client
- Copy the Client secret value
- Update the
clientSecretfield inrhcl-operator/oidc-policy.yamlwith this value - Commit and push the change to your repository for ArgoCD to sync
Note: The client secret is required for the OIDC Policy to authenticate with Keycloak. Without it, the OIDC authentication flow will fail.
Step 5: Create OpenShift Route for Gateway (Manual)
The Gateway API Gateway resource (neuralbank-gateway) needs an OpenShift Route to expose it externally. This step must be done manually from the OpenShift console or CLI.
Option 1: Using OpenShift Console
- Navigate to Networking → Routes in the
istio-systemnamespace - Click Create Route
- Configure the route:
- Name:
neuralbank-external-route(or your preferred name) - Hostname:
neuralbank.apps.<your-cluster-domain>(or use a wildcard*.apps.<your-cluster-domain>) - Service: Select
neuralbank-gateway-istioservice - Target Port: Select
http(port 8080) - TLS Termination: Edge
- Insecure Traffic: Redirect
- Name:
Option 2: Using CLI
You can also create the route using oc:
oc create route edge neuralbank-external-route \
--service=neuralbank-gateway-istio \
--hostname=neuralbank.apps.<your-cluster-domain> \
--port=http \
--namespace=istio-system
For Wildcard Route:
If you want to use a wildcard route to access both frontend and backend through the same hostname:
oc create route edge neuralbank-external-route \
--service=neuralbank-gateway-istio \
--hostname="*.apps.<your-cluster-domain>" \
--port=http \
--namespace=istio-system
Note: The wildcard route allows you to access the application using any subdomain under apps.<your-cluster-domain>, which is useful for development and testing. The Gateway and HTTPRoute resources will handle the actual routing based on the hostnames specified in the HTTPRoute manifests.
📁 Repository Structure
Top-Level Files
applicationset-instance.yaml— ArgoCD ApplicationSet/instance manifest that ties multiple applications togetherupdate-cluster-domain.sh— Bash script to automatically update cluster domain references (legacy method; recommended: use ApplicationSets with Kustomize patches as described in Configuration)
Developer Hub (developer-hub/)
Red Hat Developer Hub (Backstage) configuration and manifests:
developer-hub/README.md— Developer Hub app configuration and notesdeveloper-hub/app-config.yaml— Backstage application configurationdeveloper-hub/backstage.yaml— Backstage Kubernetes deployment manifestdeveloper-hub/dynamic-plugins.yaml— Dynamic plugin configurationdeveloper-hub/kustomization.yaml— Kustomize overlay for developer-hubdeveloper-hub/ols-embeddings.yaml— Embeddings/ML integration configurationdeveloper-hub/rcsconfig-onprem.yaml— RCS on-premises configurationdeveloper-hub/rcsconfig.yaml— RCS cloud configurationdeveloper-hub/rhdh-rbac-policy.yaml— RBAC policy for Developer Hubdeveloper-hub/rolebinding.yaml— RoleBinding for the app namespacedeveloper-hub/secret-secrets-rhdh.yaml— Secrets manifest for Developer Hub
NeuralBank Stack (neuralbank-stack/)
Helm chart for the NeuralBank demo application (frontend, backend, database, and proxy):
neuralbank-stack/Chart.yaml— Helm chart metadataneuralbank-stack/values.yaml— Helm chart default values (includes Keycloak and API configuration)neuralbank-stack/templates/— Kubernetes manifest templates:backend.yaml— Backend service deploymentdb-deployment.yaml— PostgreSQL database deploymentdb-resources.yaml— Database persistent volume and servicefrontend.yaml— Frontend application deploymentneuralbank-config.yaml— ConfigMap with runtime configuration (Keycloak URLs, API endpoints)proxy.yaml— Nginx reverse proxy/gateway configurationroute.yaml— OpenShift Route for external accesssa-default.yaml— Service account definitionsrolebinding.yaml— RBAC bindingsscc-rolebinding.yaml— Security context constraints
Operators (operators/)
Helm charts for operators used in the demo:
operators/Chart.yaml— Helm chart metadataoperators/helm-values.yaml— Operator configuration valuesoperators/templates/— Operator subscription and configuration manifests:rhbk.yaml— Red Hat Build of Keycloak operator subscriptionrhcl-operator.yaml— Red Hat Connectivity Link operator subscriptionrhdh.yaml— Red Hat Developer Hub operator subscriptionservicemeshoperator3.yaml— Service Mesh Operator (Istio) subscriptionsubscriptions.yaml— Operator subscription definitions
operators/tests/— Helm chart tests
Red Hat Build of Keycloak (rhbk/)
Keycloak and related secrets/realm setup used for authentication in the demo:
rhbk/keycloak-backstage-realm.yaml— Backstage realm configuration for Keycloakrhbk/keycloak-db-secret.yaml— Database credentials secret for Keycloakrhbk/keycloak-initial-admin.yaml— Initial admin credentials for Keycloakrhbk/keycloak.yaml— Keycloak operator CR that deploys Keycloak (demo configuration)rhbk/postgres.yaml— PostgreSQL database for Keycloakrhbk/kustomization.yaml— Kustomize configurationrhbk/rolebinding.yaml— RBAC bindings for Keycloak namespace
RHCL Operator (rhcl-operator/)
Red Hat Connectivity Link operator configurations for API gateway, OIDC authentication, and authorization policies:
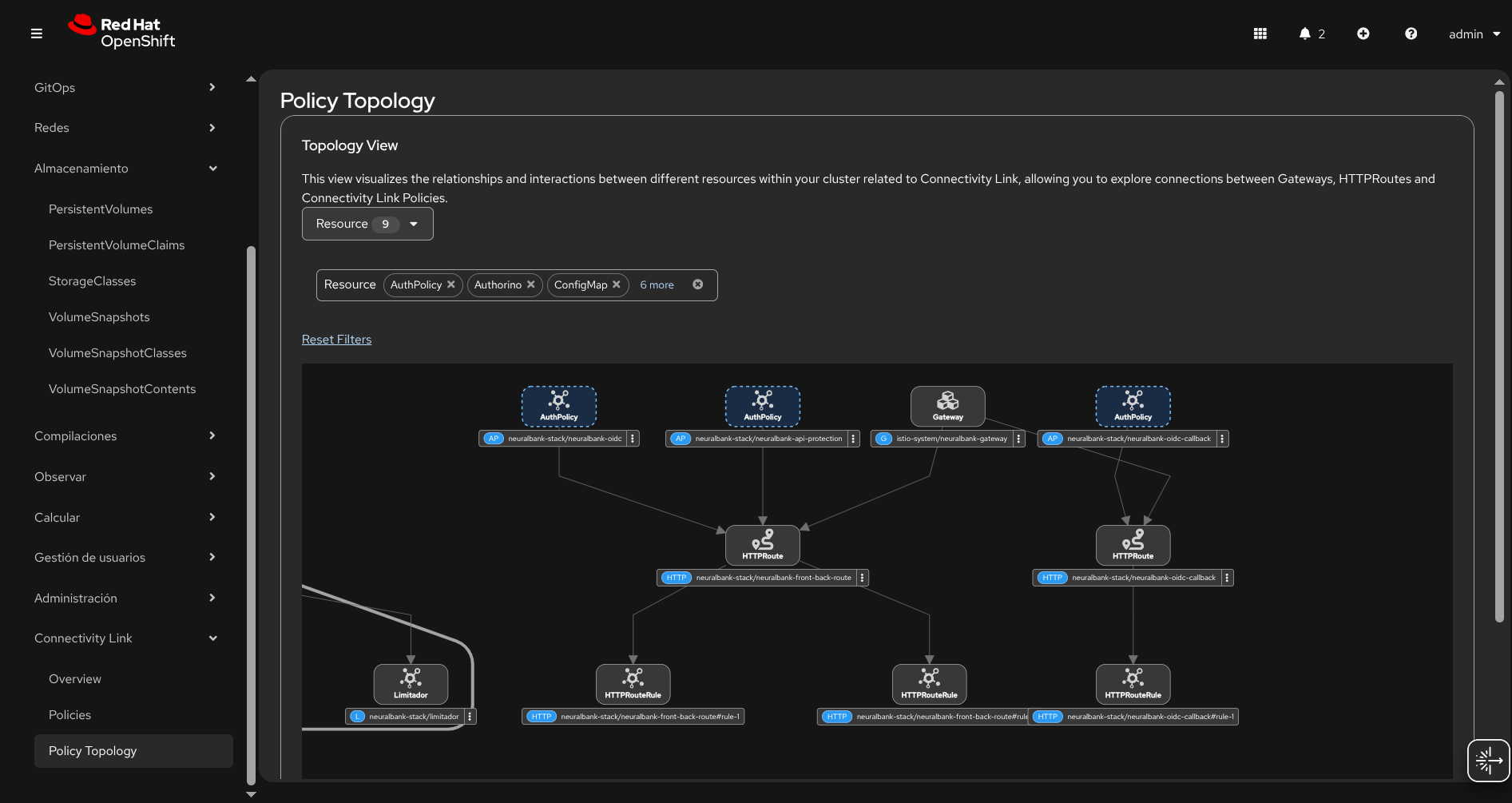
rhcl-operator/kustomization.yaml— Kustomize configuration for RHCL resourcesrhcl-operator/kuadrant.yaml— Kuadrant CR (manages Authorino for OIDC authentication)rhcl-operator/oidc-policy.yaml— OIDCPolicy CR defining OIDC authentication flow (issuer, client credentials, endpoints)rhcl-operator/neuralbank-route.yaml— Kubernetes Gateway API HTTPRoute resources:neuralbank-api-route— Routes/apiand/qpaths to backend serviceneuralbank-root-route— Routes root path and static assets to frontend service
rhcl-operator/neuralbank-oidc-callback.yaml— HTTPRoute for OIDC callback endpoint (/auth/callback)rhcl-operator/keycloak-authpolicy.yaml— AuthPolicy CR for advanced authentication rules and token handlingrhcl-operator/rolebinding.yaml— RBAC bindings for ArgoCD to manage RHCL resources
Key Features:
- OIDC-based authentication using Keycloak as the identity provider
- API protection with Authorino (via Kuadrant)
- Gateway API HTTPRoute definitions for traffic routing
- Token-based authorization with cookie and header support
HTTPRoute Resources
The HTTPRoute resources define how traffic is routed from the Gateway to backend services. These routes use the Kubernetes Gateway API standard and are managed by the Istio Gateway implementation.
Structure:
parentRefs: References the Gateway resource (neuralbank-gatewayinistio-systemnamespace) that will handle the traffichostnames: Specifies the hostname(s) that this route will match (must match the OpenShift Route hostname)rules: Defines path-based routing rules:matches: Path patterns to match (e.g.,/api,/q,/)backendRefs: Kubernetes Service to route matched traffic to
Example HTTPRoute (neuralbank-api-route):
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: neuralbank-gateway
namespace: istio-system
hostnames:
- "neuralbank.apps.<your-cluster-domain>"
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /api
backendRefs:
- name: neuralbank-backend-svc
port: 8080
This route matches requests to /api/* and /q/* and forwards them to the neuralbank-backend-svc service on port 8080.
OIDC Policy Configuration
The OIDCPolicy resource configures OIDC authentication for protected routes. It integrates with Authorino (via Kuadrant) to enforce authentication at the gateway level.
Key Configuration Fields:
provider.issuerURL: The Keycloak realm issuer URL- Format:
https://<keycloak-host>/realms/<realm-name> - Example:
https://rhbk.apps.<your-cluster-domain>/realms/neuralbank
- Format:
provider.clientID: The Keycloak client ID (must match the client configured in Keycloak)- Example:
neuralbank
- Example:
provider.clientSecret: ⚠️ IMPORTANT — The client secret generated from Keycloak console- This must be obtained from Keycloak after enabling client authentication
- Steps to get the secret:
- Log into Keycloak console
- Navigate to your realm → Clients → Select your client
- Go to the Credentials tab
- Copy the Client secret value
- Update the
clientSecretfield inoidc-policy.yaml
- Security Note: Consider using a Kubernetes Secret to store the client secret instead of hardcoding it in the YAML file
provider.authorizationEndpoint: Keycloak authorization endpoint- Format:
https://<keycloak-host>/realms/<realm-name>/protocol/openid-connect/auth
- Format:
provider.redirectURI: OAuth callback URL (must match a redirect URI configured in Keycloak client)- Example:
https://neuralbank.apps.<your-cluster-domain>/auth/callback
- Example:
provider.tokenEndpoint: Keycloak token endpoint- Format:
https://<keycloak-host>/realms/<realm-name>/protocol/openid-connect/token
- Format:
targetRef: References the HTTPRoute resource that should be protected by this OIDC policy- Example:
neuralbank-api-route(protects the/apiand/qendpoints)
- Example:
auth.tokenSource: Defines where to look for the authentication tokenauthorizationHeader: Token inAuthorization: Bearer <token>headercookie: Token stored in a cookie (e.g.,jwtcookie)
Example OIDC Policy:
spec:
provider:
issuerURL: "https://rhbk.apps.<your-cluster-domain>/realms/neuralbank"
clientID: neuralbank
clientSecret: "<your-client-secret-from-keycloak>" # ⚠️ Update this!
authorizationEndpoint: "https://rhbk.apps.<your-cluster-domain>/realms/neuralbank/protocol/openid-connect/auth"
redirectURI: "https://neuralbank.apps.<your-cluster-domain>/auth/callback"
tokenEndpoint: "https://rhbk.apps.<your-cluster-domain>/realms/neuralbank/protocol/openid-connect/token"
targetRef:
group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
kind: HTTPRoute
name: neuralbank-api-route
auth:
tokenSource:
authorizationHeader:
prefix: Bearer
name: Authorization
cookie:
name: jwt
Important Notes:
- The
clientSecretmust be updated after generating it from the Keycloak console (see Step 4) - The
redirectURImust exactly match one of the redirect URIs configured in the Keycloak client - The
hostnamesin HTTPRoute resources must match the hostname used in the OpenShift Route - All URLs (issuer, endpoints) must use HTTPS and match your cluster’s domain configuration
Service Mesh Operator 3 (servicemeshoperator3/)
Service Mesh Operator (Istio) configurations for service mesh control plane and gateway:
servicemeshoperator3/kustomization.yaml— Kustomize configuration for service mesh resourcesservicemeshoperator3/smcp-controlplane.yaml— Service Mesh Control Plane (SMCP) configuration:IstioCR — Istio control plane deployment (version v1.27.3)IstioCNICR — Istio CNI plugin configuration- ClusterRole/ClusterRoleBinding — RBAC for ArgoCD to manage Istio resources
servicemeshoperator3/gateway.yaml— Kubernetes Gateway API Gateway resource:neuralbank-gateway— Gateway with HTTP (8080) and HTTPS (443) listeners- Role/RoleBinding — RBAC for ArgoCD to manage Gateway resources in istio-system namespace
servicemeshoperator3/gateway-route.yaml— Example HTTPRoute for gateway (commented out by default)
Key Features:
- Istio service mesh control plane management
- Kubernetes Gateway API implementation
- Multi-protocol support (HTTP/HTTPS)
- Cross-namespace route support
Namespaces (namespaces/)
namespaces/namespaces.yaml— Kubernetes namespace definitions for the demo
📝 Notes
- The demo configuration uses a Keycloak operator CR (
rhbk/keycloak.yaml) to bootstrap an instance and wire it to a PostgreSQL database - Everything in this repository is intended to be applied via a GitOps controller (ArgoCD), so changes to these files represent the desired cluster state
- The service mesh and gateway configurations work together to provide:
- Traffic management and routing
- mTLS between services
- OIDC authentication at the gateway level
- API protection with fine-grained authorization policies
🏗️ Architecture Diagrams
System Architecture
The following diagram illustrates the complete system architecture, showing how all components interact:
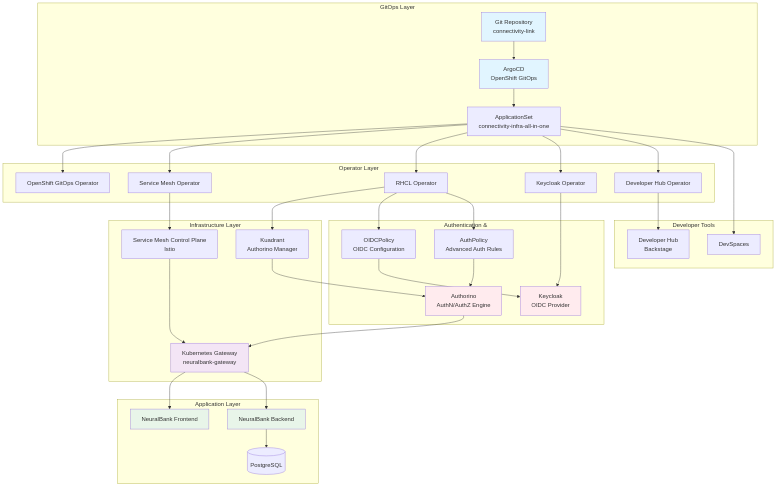
Source: docs/diagrams/system-architecture.mmd. Regenerate PNG with ./docs/generate-diagrams.sh.
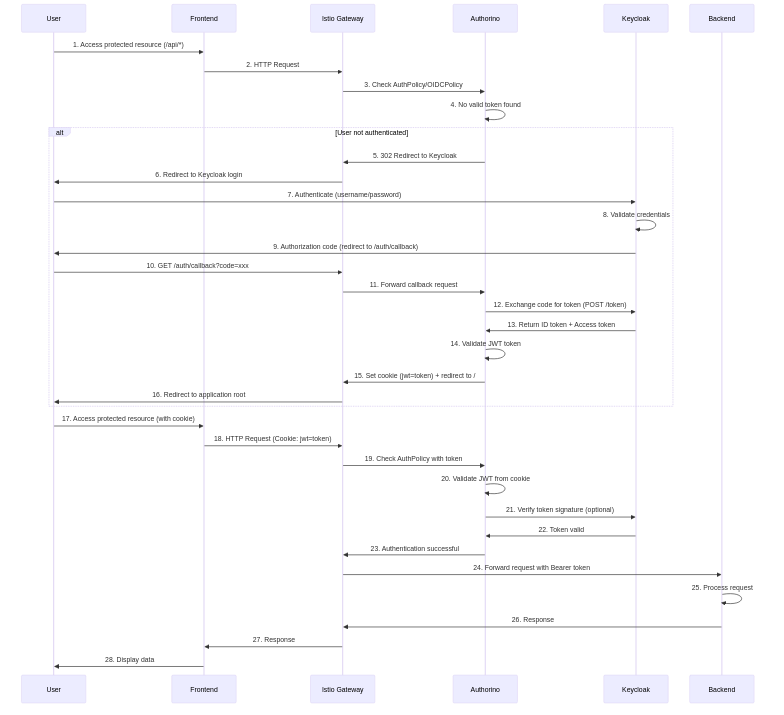
OIDC Authentication Flow
The following sequence diagram illustrates the complete OIDC authentication flow using Keycloak and Authorino:
Source: docs/diagrams/oidc-auth-flow.mmd. Regenerate PNG with ./docs/generate-diagrams.sh.
Installation Flow
The following diagram shows the automated installation process (install.sh and Ansible playbook):
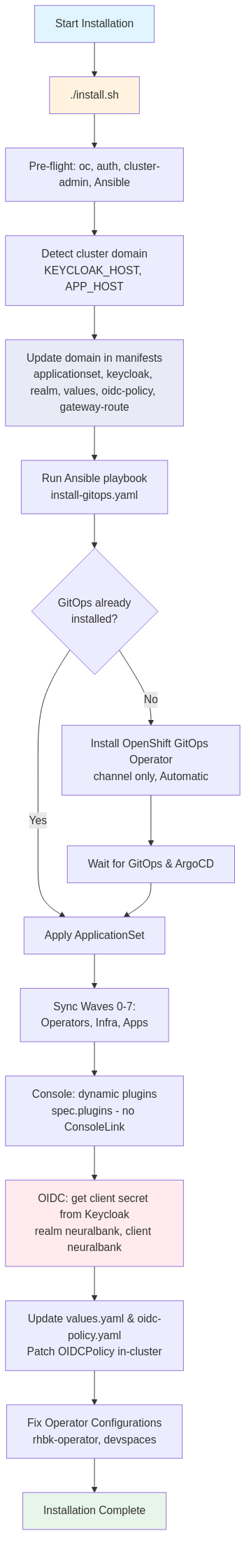
Source: docs/diagrams/installation-flow.mmd. Regenerate PNG with ./docs/generate-diagrams.sh.
The Application Solution without Auth 🙌:
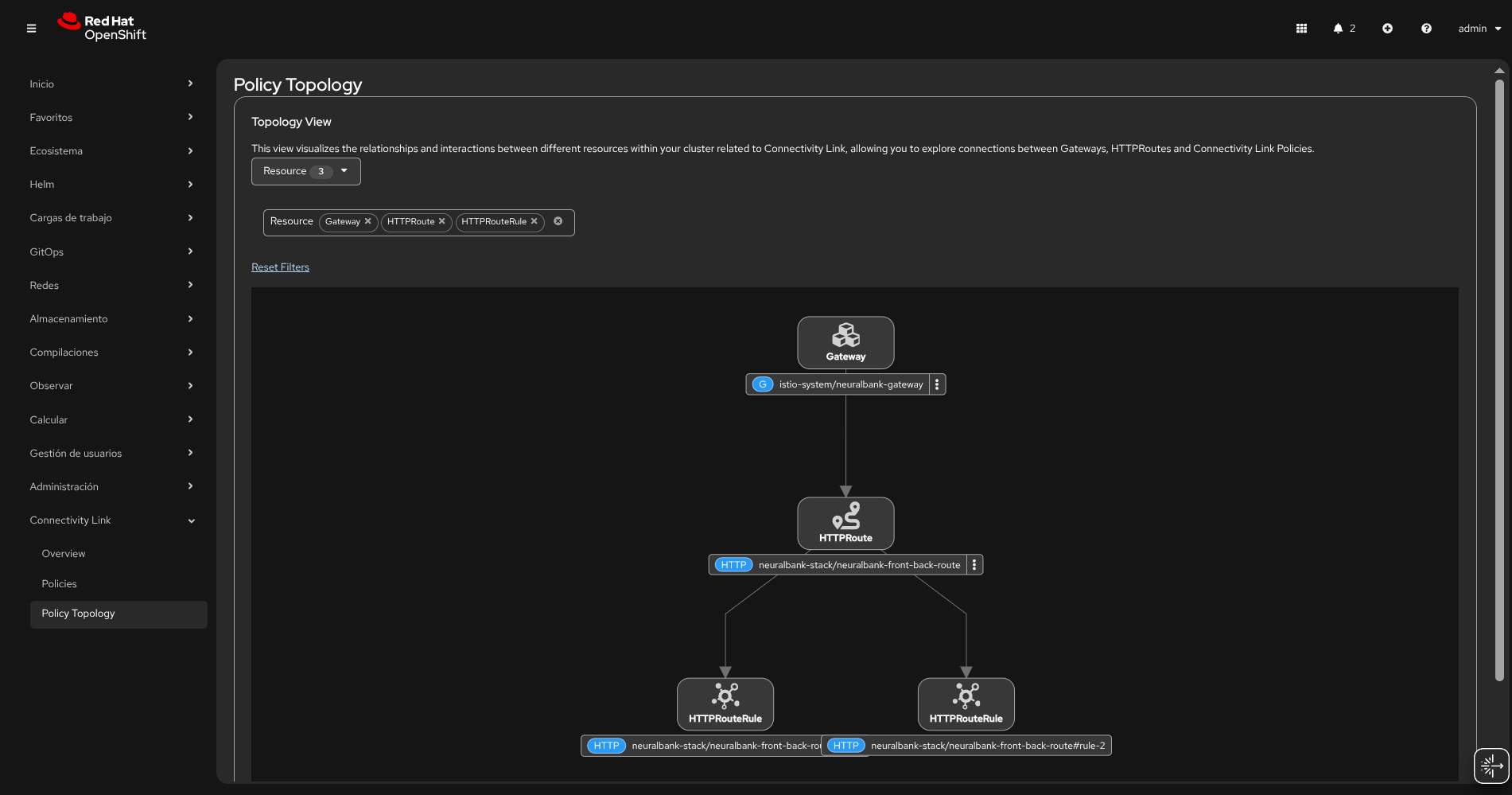
The Application Solution with Auth 🔐 powered by Red Hat Build of Keycloak & Authorino:
🌟 Benefits of Cloud Native Integration with Kuadrant
Integrating with a cloud native strategy and the Kuadrant project brings significant advantages to modern application deployment and security. The simplicity of this approach is remarkable: by adding just a few manifest files with the appropriate configuration, you can transform your application’s security posture. GitOps plays a crucial role in orchestrating these changes in a clean environment within seconds, enabling a true Zero Trust architecture implementation.
The power of this solution lies in its declarative nature—you define the desired state through Kubernetes manifests, and the GitOps workflow ensures that state is achieved and maintained automatically. This approach eliminates manual configuration errors, provides complete audit trails through Git history, and enables rapid deployment across multiple environments with consistency. The Zero Trust model is enforced at every layer: authentication through Keycloak, authorization via Authorino, rate limiting for API protection, and service mesh policies for inter-service communication. With Connectivity Link and Kuadrant, you’re establishing a comprehensive security framework that scales with your infrastructure, creating a robust foundation for modern, secure microservices architectures.
📢 Share This Content
If you found this guide helpful, please share it with your network! Help others discover how to implement Zero Trust security with Connectivity Link and GitOps.
Thank you for sharing! Your support helps the community grow and learn together.












